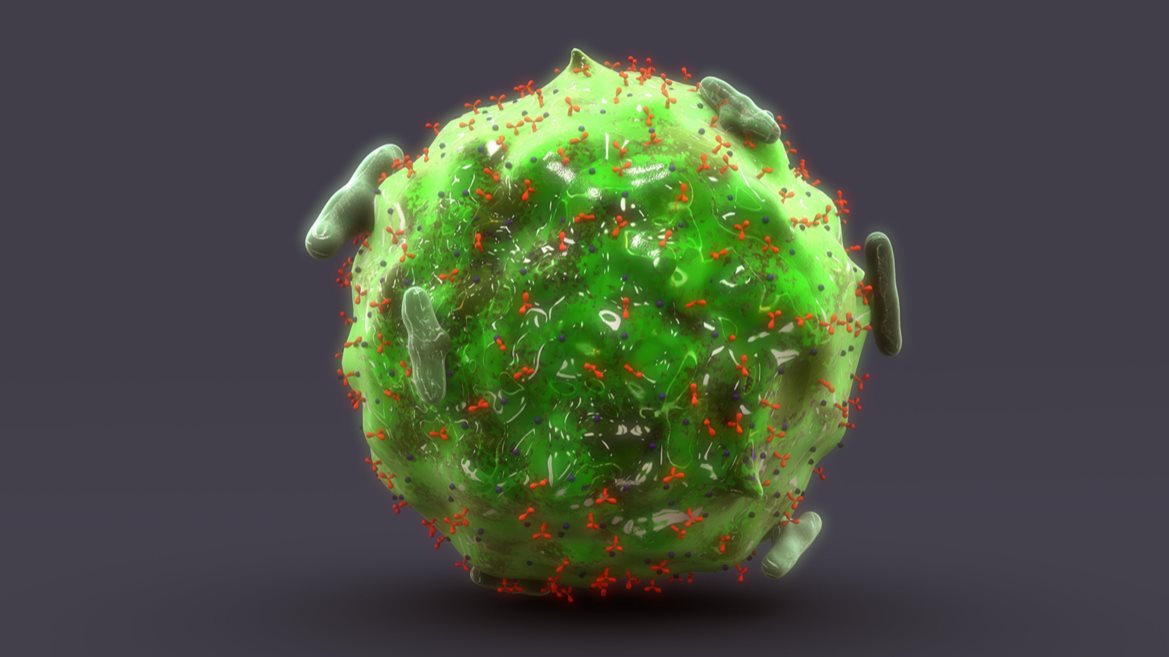
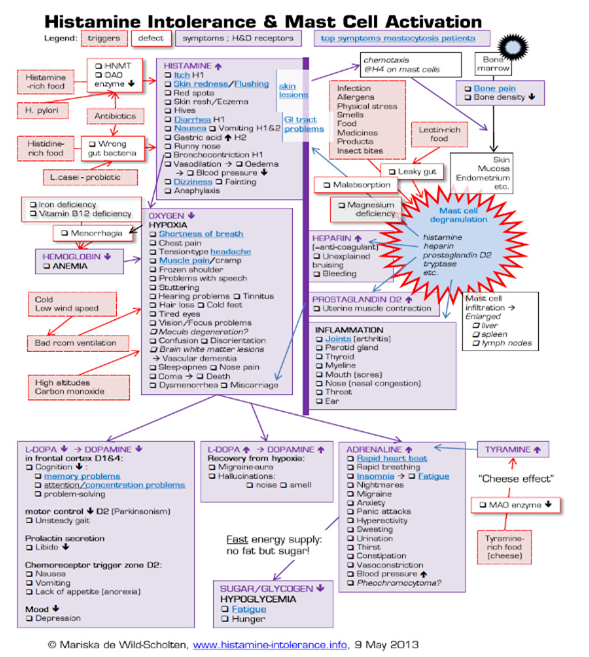
The chronic illness called Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS) describes a process in which mast cells become overreactive. It is a chronic, multi-system illness that can mimic many other diseases. Symptoms include fatigue, rash, foggy thinking, joint pain, palpitations, itchiness, insomnia, thyroid problems, gas, bloating and swollen lymph nodes.
These symptoms often boggle health care professionals who cannot make sense of how they are all related. In fact, doctors sometimes label many patients as having a psychosomatic illness or a diagnosis that these symptoms are “all in their head”. These patients can be puzzling to even integrative doctors, who treat their guts, prescribe chelation therapies, drastically change their diet and lifestyle, and treat chronic infections, only for the patients to not feel better at all.
(Please note that MCAS is very different from mastocytosis, a rare form of blood cancer.)
What are Mast Cells?
Mast cells are white blood cells that are part of our immune system. You’ll find them in all tissues but most prominently in the mucosa (our first line of defense to the outside world), and vascular tissue. Mast cells are most often seen in tissues of the gastrointestinal tract, skin, and genitourinary system but MCAS can present in all body systems. Each mast cell contains over 200 chemical signals, or cytokines, the most well-known of which is histamine.
What is the Function of the Mast Cell?
The main job of the mast cell is to connect the immune system to the nervous system, both through direct contact and indirectly, using cytokines. It is the mast cell’s job to sense things from our environment and tell our nervous system whether or not these things are a threat. If we are exposed to an infection or a toxin, the mast cell activates and releases cytokines. Cytokines tell the nervous system to ramp up and eradicate the threat.
Mast Cell Activation Syndrome Results from Hyperreactive Mast Cells
Things start to go wrong when the mast cell becomes over-responsive to “non-threats”. It can see something as simple as a food, cold temperatures, a stressful event, or even a smell as being threatening. It then overreacts and explodes, releasing all of the symptom-causing cytokines. What catalyzes this is not often known. In secondary MCAS, the trigger can be something like an infection from mold, Lyme, or a virus. Primary MCAS is usually from earlier on in life and possibly caused by ‘mutations’ in the mast cells. With so many potential toxic triggers in our world today, it’s only a matter of time before mast cells start to misbehave in a susceptible individual. When we don’t know what the cause of MCAS is, whether it be primary or secondary, we call it idiopathic MCAS. The good news is that the management for each kind of MCAS is very similar.
How Do We Diagnose MCAS?
In short, we diagnose MCAS with difficulty. You can only measure about 10 of the 200 mediators that the mast cell releases. Additionally, these mediators are in and out of the bloodstream within seconds, even though their effects are long-lasting.
Looking at the Symptoms
MCAS is often a clinical diagnosis, looking at the various symptoms that a patient has. It may be the case that the lab tests we are able to do come back as negative, but a diagnosis can still be made. However, diagnosing by symptoms is not straight-forward. Patients may present with seemingly unrelated symptoms, expressed in all systems in the body.
The symptoms will depend on which mediators are released, and in what tissues they are released. The symptoms do not always make sense and are not reproducible by the same trigger. For example, on one day a certain food may trigger a cytokine storm, but on the next day, that same food has no effect. The symptoms sometimes come on without any known trigger, and the effect can be acute or chronic, local, or remote. Patients become very scared of the symptom’s unpredictability. Many patients are misdiagnosed for years and often their entire lives.
Treatment options for MCAS
The main steps in treatment are to try find what the initial trigger is and to stabilize the mast cells. In many cases, the trigger is a chronic infection. Mold is one of the most potent mast cell triggers and is more common than you would think. Mold susceptibility is genetically determined. About 25% of people having the genes which make the body unable to recognize and clear mold when exposed. In the case of MCAS, we can stabilize mast cells, but unless we treat the mold as well, patients often won’t get better. Other examples of triggers are Lyme disease, Bartonella (a Lyme coinfection), Candida, and toxic and environmental triggers.
Identifying Triggers of MCAS
To help identify triggers, it may be useful to keep a diary of symptoms. You can then trace back the minutes and hours before a flare to figure out what may have been the trigger. In the cases of medication reactions, people often react to the fillers or inactive ingredients and not the medication itself. Sometimes there are many triggers and it is difficult to figure out what they are.
Stabilizing Mast Cells
We can stabilize the mast cells using various supplements and medications. Any given patient may respond better either to supplements or to medications, but not often both. One patient may respond beautifully to one supplement and for the next, it will have no effect. Unfortunately, it often takes some trial and error, which can be quite frustrating for patients as many of the treatments fail to work at all. Therefore, when trialing treatments, physicians must do this in a methodical way and the patient should be prepared for the fact that this can take many months to get right. The type, dosage, and frequency of treatment needs to be constantly tweaked, usually, each step taking 2-4 weeks. Also, sometimes the treatments we give for MCAS can trigger more symptoms.
Treatments for MCAS
It is important to be realistic about possible treatment outcomes. Not all patients can be completely cured of MCAS and may need treatment lifelong, especially when we do not know what the trigger is. You may not feel perfect and there may be many ups and downs, but most patients will feel better after some trial and error to create a personalized plan.
A low histamine diet may work for some, but not others. Physicians can trial for a period of 2-3 weeks and if no noted differences, will be stopped. Generally, this entails avoiding leftovers and over-ripe fruits, foods with innately high histamine, like fermented foods, aged cheese, vinegar, alcohol, and canned fish. There are also foods that easily release histamine when eaten, like strawberries, spinach, nuts, tomatoes, and shellfish. Doctors encourage patients to begin a low mold diet if mold is involved.
The treatment for MCAS can sometimes be both therapeutic and diagnostic. That is, if you get better with the treatment, you likely have MCAS, even if we have not been able to prove it in any other way.
Contact Us
Our team at Linden & Arc Vitality Institute understands that MCAS is a complex and frustrating road to travel. We are equipped to guide you on the path to your best health. If any of the above symptoms sound familiar, please contact us at [email protected] to book an appointment.
Author
Dr. Michelle van der Westhuizen, MD